Embedding noflo programs
Running via the command line
run the graph with:
noflo-nodejs --debug graphs/Canadianness.fbp
Running tests
npm test
1) the same as our tests, if we want to run in the browser
noflo = require 'noflo'
unless noflo.isBrowser()
baseDir = __dirname
else
baseDir = '/canadianness'
2) create our basic ComponentLoader:
noflo = require 'noflo'
unless noflo.isBrowser()
baseDir = __dirname
else
baseDir = '/canadianness'
# @async
canadianness = ->
loader = new noflo.ComponentLoader baseDir
# project name / graph or component name
loader.load 'canadianness/Canadianness', (err, instance) ->
throw err if err
3) create & attach our InternlSockets (these are used behind the scenes when you attach two components together)
noflo = require 'noflo'
unless noflo.isBrowser()
baseDir = __dirname
else
baseDir = '/canadianness'
canadianness = (args, cb) ->
loader = new noflo.ComponentLoader baseDir
# project name / graph or component name
loader.load 'canadianness/Canadianness', (err, instance) ->
throw err if err
instance.once 'ready', ->
instance.start()
# outPorts
score = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
emotion = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# inPorts
spelling = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
words = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
content = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# attach them
instance.inPorts.content.attach content
instance.inPorts.spelling.attach spelling
instance.inPorts.words.attach words
instance.outPorts.score.attach score
instance.outPorts.emotion.attach emotion
3) listen for the outPorts data:
noflo = require 'noflo'
unless noflo.isBrowser()
baseDir = __dirname
else
baseDir = '/canadianness'
canadianness = (args, cb) ->
loader = new noflo.ComponentLoader baseDir
# project name / graph or component name
loader.load 'canadianness/Canadianness', (err, instance) ->
throw err if err
instance.once 'ready', ->
instance.start()
# outPorts
score = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
emotion = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# inPorts
spelling = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
words = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
content = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# attach them
instance.inPorts.content.attach content
instance.inPorts.spelling.attach spelling
instance.inPorts.words.attach words
instance.outPorts.score.attach score
instance.outPorts.emotion.attach emotion
scoreData = null
emotionData = null
score.on 'data', (data) ->
scoreData = data
emotion.on 'data', (data) ->
emotionData = data
4) arguments
noflo = require 'noflo'
unless noflo.isBrowser()
baseDir = __dirname
else
baseDir = '/canadianness'
canadianness = (args, cb) ->
spellingData = args['spelling']
wordsData = args['words']
# debugging [optional]
debug = args['debug'] or false
contentData = args['content']
loader = new noflo.ComponentLoader baseDir
# project name / graph or component name
loader.load 'canadianness/Canadianness', (err, instance) ->
throw err if err
instance.once 'ready', ->
instance.start()
# outPorts
score = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
emotion = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# inPorts
spelling = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
words = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
content = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# attach them
instance.inPorts.content.attach content
instance.inPorts.spelling.attach spelling
instance.inPorts.words.attach words
instance.outPorts.score.attach score
instance.outPorts.emotion.attach emotion
# scoped variables since we don't know which data comes in first
scoreData = null
emotionData = null
score.on 'data', (data) ->
scoreData = data
if emotionData
cb emotionData, scoreData
emotion.on 'data', (data) ->
emotionData = data
if scoreData
cb emotionData, scoreData
5) debugging:
using flowtrace
noflo = require 'noflo'
trace = require('noflo-runtime-base').trace
unless noflo.isBrowser()
baseDir = __dirname
else
baseDir = '/canadianness'
canadianness = (args, cb) ->
spellingData = args['spelling']
wordsData = args['words']
# debugging [optional]
debug = args['debug'] or false
contentData = args['content']
loader = new noflo.ComponentLoader baseDir
# project name / graph or component name
loader.load 'canadianness/Canadianness', (err, instance) ->
throw err if err
if debug
# instantiate our Tracer
tracer = new trace.Tracer()
instance.once 'ready', ->
if debug
tracer.attach instance.network
instance.start()
# outPorts
score = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
emotion = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# inPorts
spelling = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
words = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
content = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# attach them
instance.inPorts.content.attach content
instance.inPorts.spelling.attach spelling
instance.inPorts.words.attach words
instance.outPorts.score.attach score
instance.outPorts.emotion.attach emotion
# scoped variables since we don't know which data comes in first
scoreData = null
emotionData = null
# when we listen for data, we can call this
# to check if both have received data
# when they have, call the callback
# and then, if we are debugging, write the trace
# and log where we wrote it to
finished = ->
return unless scoreData? and emotionData?
cb emotionData, scoreData
if debug
tracer.dumpFile null, (err, f) ->
throw err if err
console.log 'Wrote flowtrace to', f
# listen for data
score.on 'data', (data) ->
scoreData = data
finished()
emotion.on 'data', (data) ->
emotionData = data
finished()
# send the data
words.send wordsData
spelling.send spellingData
content.send contentData
6) using it:
noflo = require 'noflo'
trace = require('noflo-runtime-base').trace
unless noflo.isBrowser()
baseDir = __dirname
else
baseDir = '/canadianness'
canadianness = (args, cb) ->
spellingData = args['spelling']
wordsData = args['words']
# debugging [optional]
debug = args['debug'] or false
contentData = args['content']
loader = new noflo.ComponentLoader baseDir
# project name / graph or component name
loader.load 'canadianness/Canadianness', (err, instance) ->
throw err if err
if debug
# instantiate our Tracer
tracer = new trace.Tracer()
instance.once 'ready', ->
if debug
tracer.attach instance.network
instance.start()
# outPorts
score = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
emotion = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# inPorts
spelling = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
words = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
content = noflo.internalSocket.createSocket()
# attach them
instance.inPorts.content.attach content
instance.inPorts.spelling.attach spelling
instance.inPorts.words.attach words
instance.outPorts.score.attach score
instance.outPorts.emotion.attach emotion
# scoped variables since we don't know which data comes in first
scoreData = null
emotionData = null
# when we listen for data, we can call this
# to check if both have received data
# when they have, call the callback
# and then, if we are debugging, write the trace
# and log where we wrote it to
finished = ->
return unless scoreData? and emotionData?
cb emotionData, scoreData
if debug
tracer.dumpFile null, (err, f) ->
throw err if err
console.log 'Wrote flowtrace to', f
# listen for data
score.on 'data', (data) ->
scoreData = data
finished()
emotion.on 'data', (data) ->
emotionData = data
finished()
# send the data
words.send wordsData
spelling.send spellingData
content.send contentData
canadianness {spelling: spellingData, words: listData, content: 'eh', debug: true}, (score, emotion) ->
console.log score, emotion
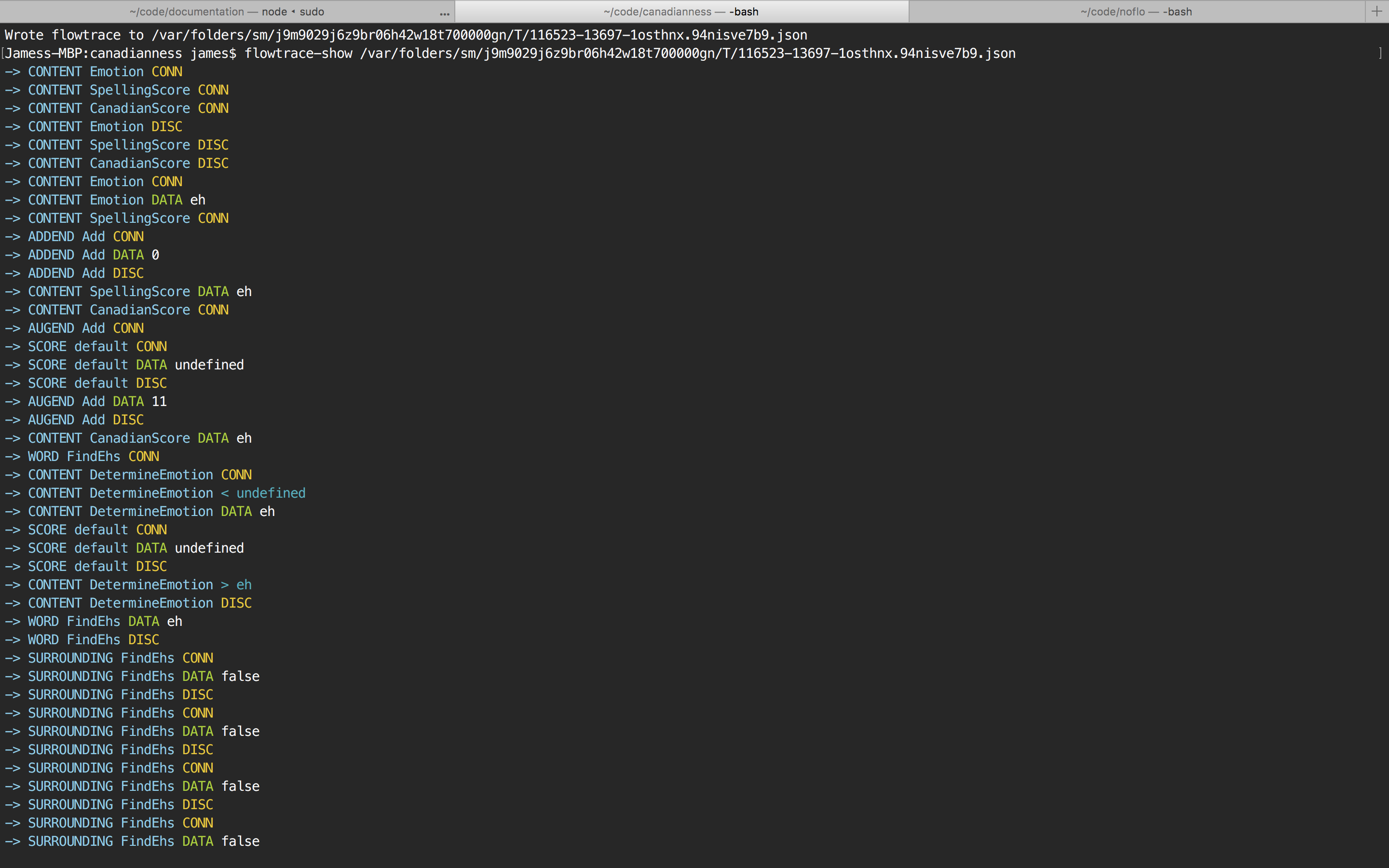
when the flowtrace has been written, we can copy and paste the location of that log and then show the trace:
$ flowtrace-show <JSON-TRACE-LOCATION>
7) Shorter
now that you know how to do it yourself, if you choose, you can use a library to achieve the same thing more easily, fbp-spec
Tester = require 'noflo-tester'
canadianness = (args, cb) ->
spellingData = args['spelling']
wordsData = args['words']
# debugging [optional]
debug = args['debug'] or false
contentData = args['content']
ness = new Tester 'canadianness/Canadianness', trace: true
ness.start (err, instance) ->
return throw err if err
# using noflo-tester, you can
# [receive from multiple outports](https://github.com/trustmaster/noflo-tester#receiving-from-multiple-output-ports)
scoreData = null
emotionData = null
ness.receive
score: (data) ->
scoreData = data
remainder: (data) ->
emotionData = data
.then ->
cb emotionData, scoreData
# send the data
# send an object to Tester, the properties are the ports
ness.send
words: wordsData
spelling: spellingData
content: contentData